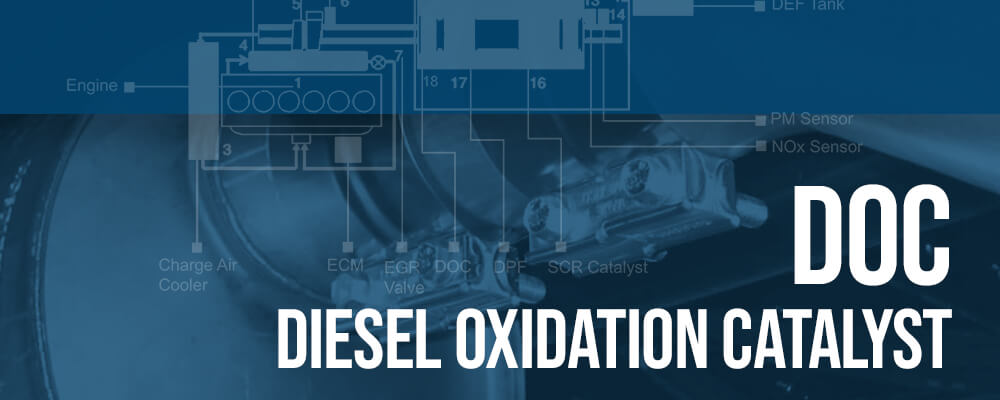
Since 2006, Diesel Emissions Service has been servicing commercial equipment with aftertreatment systems. There are four components of the aftertreatment system, which is also referred to as the diesel emissions system. It is important that whoever is performing maintenance and repairs on your aftertreatment system understands how the four components of the system work. Over the years we have received several questions specifically about the DOC that we wanted to answer in this article.
What Does the DOC Stand for in Diesel Engines?
The DOC in a diesel engine stands for Diesel Oxidation Catalyst.
Understanding the Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC)
The DOC is designed to convert carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide and water. It essentially breaks down pollutants in the exhaust system from a diesel engine which helps reduce particulate matter.
How it works:
The exhaust flows straight through the DOC substrate with very little restriction. In the aftertreatment system, there is a hydrocarbon dosing system where fuel is dosed at a specific temperature; the fuel turns into a vapor and that vapor starts the chemical reaction which produces heat. The ECM has a thermal management system where it maintains that heat and this process allows the diesel particulate filter to operate at peak performance.
Can the DOC be Cleaned like a Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF)?
Yes, anytime the DPF is removed for cleaning, the DOC should be removed, inspected, and cleaned as well. It is recommended to follow the same cleaning method as the DPF. When technicians see a DPF fault code many times they will focus on cleaning the DPF but leave the DOC in place. This is a mistake because the DOC is a flow-through device. Therefore, what is in the filter has passed through the DOC and it should be cleaned as well. If the DOC is not clear, it can become face plugged and this is part of a bigger problem that needs to be diagnosed.

Why Does a DOC Fail?
DOCs are coated with precious metals and over time these deteriorate causing the DOC to fail. The DOC has no moving parts, resulting in it having a long lifecycle. Therefore 80% of DOC and DPF failures are premature due to engine-related issues.
The DOC has one job, which is to create heat for soot oxidation, but if the engine is not running properly because of bad injectors or a turbo issue, or the aftertreatment system is not operating properly due to exhaust leaks or a leaking hydrocarbon doser, the DOC will fail prematurely. We will see DOC contamination which in turn could poison the DOC and cause DOC face plugging.
What is DOC Face Plugging?
Face plugging is an extreme buildup of carbon on the inlet side of your DOC. This extreme buildup causes additional exhaust backpressure and restricts exhaust flow, which hinders the performance of the DPF and SCR downstream.
The Key to Aftertreatment System Maintenance
Regardless of what component of the aftertreatment system you are working on, the most important thing you need to remember about aftertreatment system maintenance is this:
“Upstream problems in the system are often the cause of downstream failures.”
It is so important to look at the entire aftertreatment system when diagnosing problems, but beyond that, it is equally important to look at the other engine systems as well.
At Diesel Emissions Service our focus is mainly on fleets in California, Oregon, and British Columbia, if you require a comprehensive aftertreatment maintenance, DPF cleaning, and repair service, contact us today.
We hope you found this article helpful. At DES, we believe in putting out educational and informative content to not only our customers but for the general industry to grow and benefit from.
To share this article, use one of the social media icons above.

